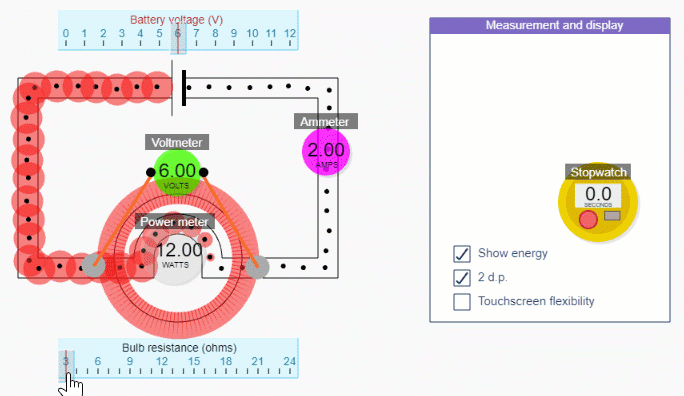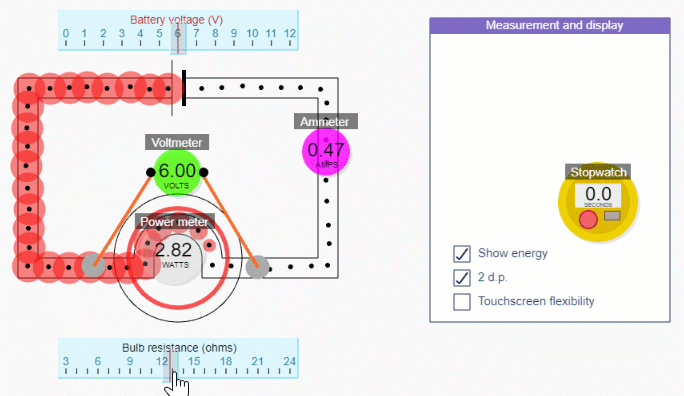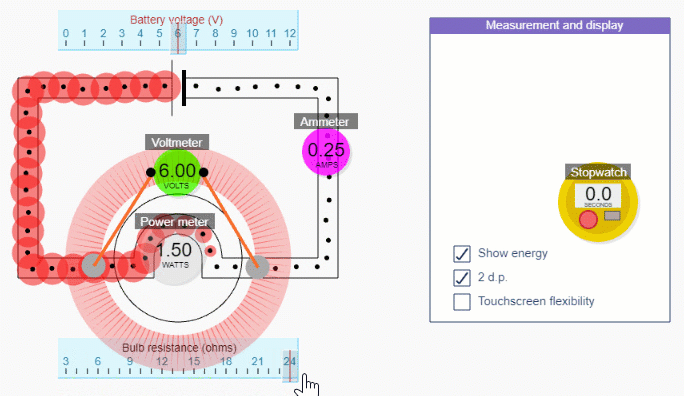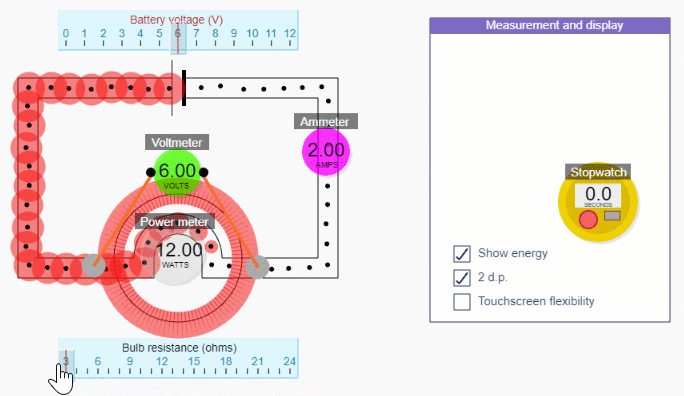
Check out what you get with a subscription
Enrich your teaching with a subscription. Three simulations, 90+ visualisations, 50+ videos, interactive quizzes and printable support materials at your fingertips.
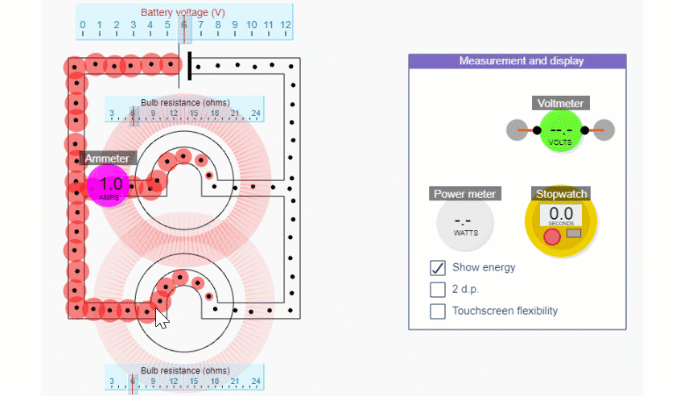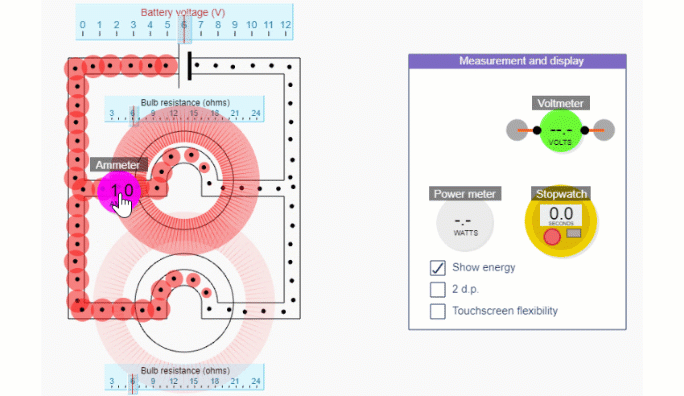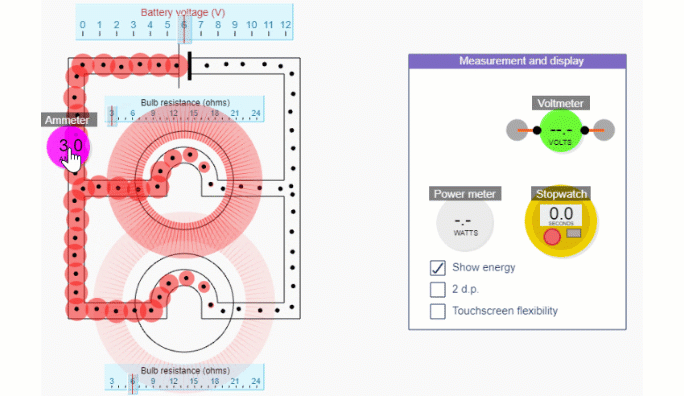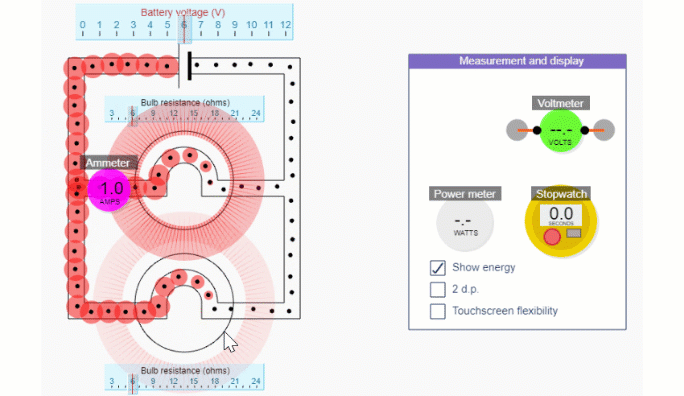
Series and Parallel circuit simulations
Simple circuit simulation
Series circuit simulation
Parallel circuit simulation
Charge and current topics
1. Current and flow
Round and round we go
1.1 Electric current is the flow of charged things
1.2 In metal wires it’s electrons that are flowing
1.3 Electron flow is very slow
1.4 You need a power source and a complete circuit
Demo lesson
A bit like speed, but not quite the same
2.1 Current as coulombs of charge passing a point each second
2.2 Measuring current by timing charges | Equation I=Q/t
2.3 I=Q/t example calculation
2.4 Conventional current: Imagining all charges are positive and move from positive to negative
2.5 Using an ammeter: Put it in the way of the current you want to measure
3. Calculating charge | Q=It
Counting charges as they drift past
3.1 It’s hard to measure charge, but you can calculate it
4. Current in series and parallel circuits
Can’t make it, can’t lose it
4.1 Current can’t appear or disappear
4.2 Beware the constant current misconception
Voltage and p.d. topics
5. Voltage | V=E/Q
Batteries keep it constant
5.1 Batteries and energy stores
5.2 Voltage as energy per charge
5.3 Calculating voltage using V=E/Q
6. Voltage in series circuits
Sharing a fixed cake
6.1 Using a voltmeter to measure potential difference
6.2 The voltage always drops to zero as you go round a circuit
6.3 The bigger the resistance, the bigger the share of the voltage
7. Voltage in parallel circuits
Parallel - the natural way
7.1 The p.d. across parallel branches is equal to the battery voltage
7.2 Everything in your home is connected in parallel with the mains
Resistance and Ohm’s Law topics
8. Resistance | R=V/I
Big resistance, small current
8.1 Conductors have low resistance, insulators have high resistance
8.2 Mobile electrons or ions make things conductors
8.3 Calculating resistance using R=V/I
9. Ohm’s Law for a wire
A law rarely obeyed
9.1 How current changes with voltage in a wire
9.2 Ohm’s law - when a component has a constant resistance
10. Current vs. voltage for a filament bulb
It’s hot work
10.1 Investigating the I-V behaviour of a filament bulb
10.2 I-V curves and resistance
11. Temperature and resistance
The warmth makes the current sleepy
11.1 A simple model of temperature and resistance
12. Diodes, thermistors and LDRs
Take control
12.1 Diodes and current direction
12.2 Diode I-V graph by experiment
12.3 Photocell switches and thermostats
12.4 Investigation: Thermistor resistance vs. temperature
12.5 Investigation: LDR resistance vs. brightness
12.6 Thermistors and LDRs in potential dividers
Power and heating topics
13. Electrical power | P=IV
How fast, not just how much
13.1 Power tells you how fast energy is shifted
13.2 Electrical power depends on both current and voltage
14. Electrical heating
Making a virtue of necessity
14.1 Heating by design and heating by accident
14.2 More ways to write the electrical power equation
Domestic electricity topics
15. Basic mains electricity
Back and forth, not round and round
15.1 AC electricity in the home
16. Plugs and mains wiring
Conduct well or not at all
16.1 Plug design and electrical safety
17. Fuses and earthing
Weakness makes the system stronger
17.1 Electric shocks and how to avoid them
17.2 Electric fire hazards and how to avoid them
17.3 The earth wire helps the fuse blow
17.4 Choose the lowest fuse above the working current
18. Circuit breakers and residual current devices
A chance to reset
18.1 Fuse boards are the start of all your household wiring
18.2 Mechanical circuit breakers trip with big currents
18.3 Residual current devices trip when current leaks